If you're a health professional you should know that you can't implicitly trust medical news outlets. They may be manipulating you!

Do Collagen Supplements Work?
Table of Contents
- Does Collagen Work?
- How Does Collagen Work?
- Does Collagen Supplementation Work?
- Are Collagen Peptides (Powders, Pills, Bars, etc.) Effective?
- Do Collagen Supplements Work for Skin?
- Do Collagen Supplements Work for Joints?
- Can collagen supplements have similar results as eating foods with collagen?
- Select Research on Collagen
- Related Articles
Why do dogs chew on bones? Well, many speculate that it’s mainly for keeping their teeth clean. But there’s another reason: collagen, the strong yet supple and resilient material that connects your bones, keeps your skin looking youthful and healthy, and—as the most abundant protein in your body—serves as the structure that holds your body together. So let’s talk about this miracle tissue and why we need to include it in our diet.
Does Collagen Work?
I get this question a lot. Usually, when people are asking this, they’re really asking if collagen supplements work. Will get to that question a little later. But let’s explore this question taken at face value: Does collagen work? Let’s put it this way, collagen works so well that it has become, over many hundreds of thousands of years, essential to the human body. It has been suggested that one of the key benefits of the use of fire for cooking relates to collagen.
Collagen is the most abundant protein in the bodies of our prey animals and it’s only present in animals. Plants are devoid of collagen. In his book, Catching Fire, Richard Wrangham suggests that the advent of fire (and cooking) was a perfectly suited method for increasing our collagen and therefore our total protein intake. Collagen is so strong that it has more tensile strength than steel, and requires a lot of work on the part of our digestive system. Nature had at least partly solved this problem by making our digestive system larger.
This article is continued below...(scroll down)
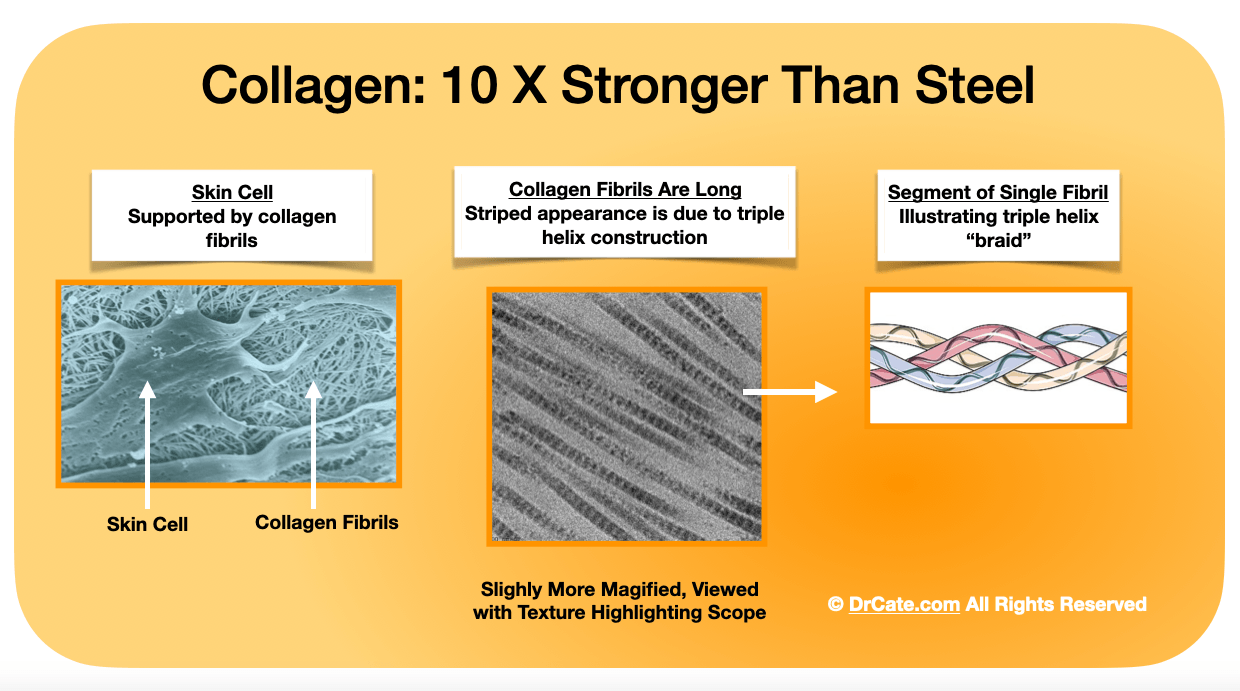
When fire entered the picture, this flipped a key evolutionary switch. Fire softens collagen, making it soft enough for us to consume and digest with significantly less intestinal yardage. According to the “expensive tissue hypothesis,” less intestine allowed the same amount of protein to be devoted to building more brain. Our brain size has nearly tripled since the advent of fire, according to some estimates.
So necessary is collagen to human health that much of our dietary history has been devoted to its extraction and acquisition. From the ancient and intricate Argentinian open fire techniques made famous world-renowned chef Francis Mallmann, to Genghis Kahn’s army’s practice of tenderizing tough (collagen-rich) meat by riding all day with thin slices under their saddles, to the simple act of boiling bones and joint material in water to make soup—one could say that collagen is what holds the modern human’s nutritional story together.
Until relatively recently, in fact, collagen was a major part of our diets. Fannie Farmer’s 1986 Cook Book has no fewer than six recipes for tripe, that collagen-rich, rubbery honeycombed part of a cow stomach that is a key ingredient to making Mexico’s national dish, Menudo.

So saying that collagen works is, as you can see, a bit of an understatement. It works like air, water, sleep, and sunlight work.
How Does Collagen Work?
Collagen has special health-giving powers thanks to compounds in collagen-rich tissues that are absent from the rest of the edible world.
These compounds include glycosaminoglycans, hyaluronic acid, proteoglycans, and bioactive peptides all of which are unique to collagen-rich tissues. They have been laboratory tested individually and in various combinations and shown to have the capacity to pass through the digestive system, travel through the bloodstream to enter and activate fibroblasts, a type of cell in our skin, joints, bones, and other connective tissues that manufactures collagen. In other words, these compounds have hormone-like effects.
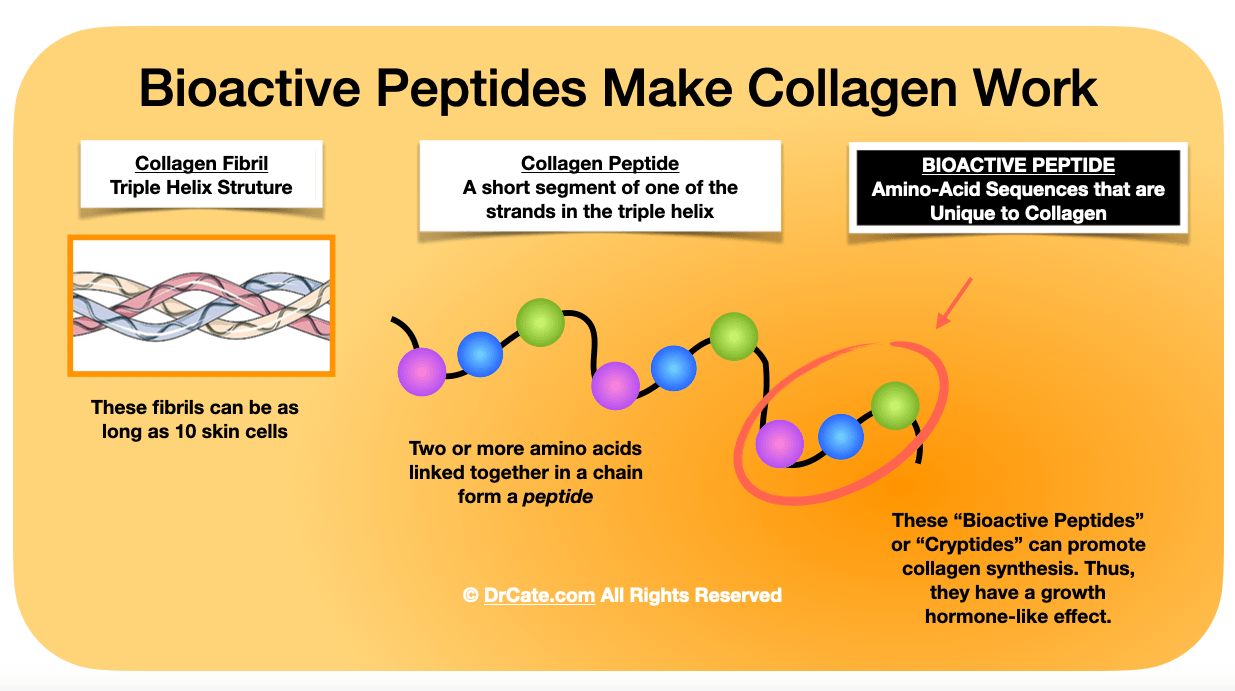
It’s not that our bodies stop making collagen if we don’t ingest it. It’s that we seem to make less of it. And given that collagen damage to our joints is the number one cause of age-related disability, and collagen damage in our arteries can cause fatal aneurysms, heart attacks, and strokes, I recommend you do everything you can to support your body’s ability to make as much collagen as it can.
Does Collagen Supplementation Work?
Let’s first talk about what we mean by supplementation. The idea of supplementing speaks to the idea of providing your body with something it needs but is not already getting. Most supplements people ask me about don’t do you any good simply because they’re compounds your body makes better than what factories can bottle. So you’re better off spending money on better quality food than on most supplements.
But collagen is different from most supplements because most Americans are woefully undernourished when it comes to collagen. Why? Dietary recommendations handed down from the so-called experts since the middle of the last century have effectively removed three key components from our healthy diet: collagen, natural fat, and salt. Say goodbye to a delicious slow-roasted turkey leg with homemade gravy (rich in the three healthy ingredients I just mentioned). Say hello to a dry slab of skinless, boneless chicken breast (specifically bred, btw, to be ultra-tender, meaning it contains less collagen).
We used to get massive amounts of collagen, and other components of connective tissue, through diet. Just like we used to spend a lot more time in the sun. But because most of us are getting so little of those things today, our bodies are particularly receptive to the benefits of supplementation with collagen as they are with vitamin D.
And although other mammals, like gorillas, for example, have retained their ability to synthesize collagen while living on a largely plant-based diet, we can’t, just as we can’t synthesize vitamin C, as dogs and cats can. And so we need to get these things from our diet, or some form of supplementation.
But as with any supplement, how the supplement is produced can make a huge difference.
Are Collagen Peptides (Powders, Pills, Bars, etc.) Effective?

All collagen powders are composed mostly of collagen peptides. Peptides are defined by two or more (up to fifty) amino acids linked together. Link a bunch of peptides together, and you get a protein.
So the big question is, If you take in collagen in the form of peptides, can your body use these building-block peptides to construct collagenous tissue? Studies strongly suggest that, yes, collagen peptides, which can be processed to a powder form easily dissolvable in water or included as an ingredient in collagen bars and other food products, can be taken up by the body and utilized to protect, build and maintain the connective tissues that makeup joints and skin.
I’ve included just a sampling of the research here to show what we’ve found about the answers to these questions:
Do Collagen Supplements Work for Skin?
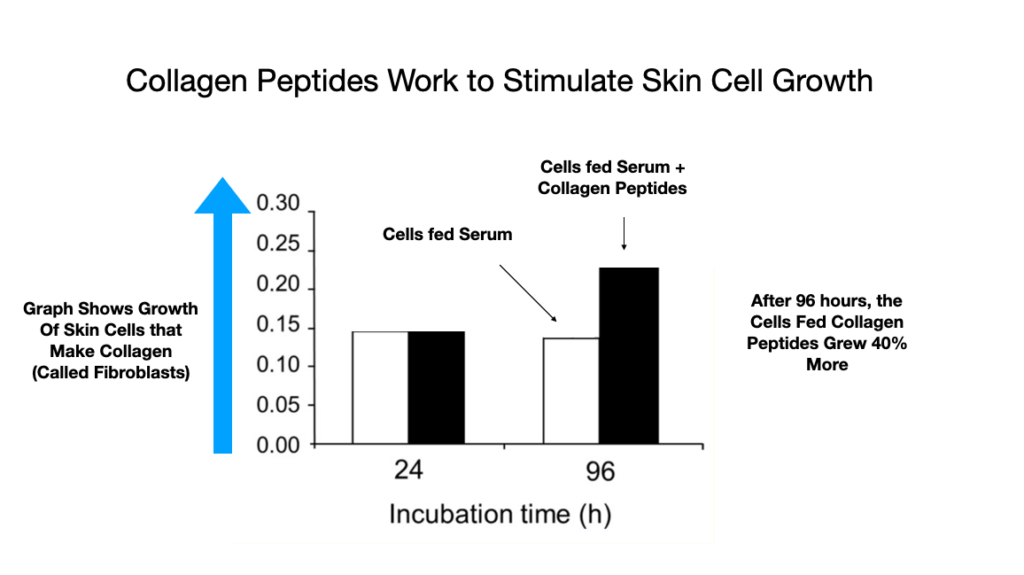
There is a lot of research in this area. This is just one of a number of articles showing the beneficial effects of collagen supplements on the skin, specifically the skin cells called fibroblasts responsible for creating the collagen that holds your skin cells together. The more collagen you have in your skin, the more supple and puncture-resistant your skin.
Do Collagen Supplements Work for Joints?
There’s also tons of research in this area. Interestingly, there’s more research on collagen for joint health in veterinary medicine than there is for us humans thanks to medical advances for thoroughbred horses and the fact that dogs participate in medical research more often than people do. As is the case for skin, components of collagen supplements including collagen hydrolysate, glycosaminoglycans, and hyaluronic acid, among others, have been shown to support fibroblast cells in various joint tissues in the same manner as with skin. (See Select Research on Collagen, below)
Can collagen supplements have similar results as eating foods with collagen?
If you’ve read my books, Deep Nutrition, Food Rules, and The Fatburn Fix, you already know that my instinct is to say that nothing can begin to compare to getting all your essential nutrition from a nutrient-dense diet based on the four pillars of traditional, ancestral foods. When I introduced homemade bone stock to the LA Lakers, only the trainers and the head chef, Sandra Padilla, appreciated its benefits. But then, when Kobe Bryant and other stars publicly vocalized their belief in the palpable benefits of collagen-rich stock, the NBA—and the larger pro-sports community—got fully on board, everything changed. Bone stock became the new superfood, the ancestral elixir every bit as necessary for growth and recovery as protein.
That said, collagen supplements, it turns out, can offer similar benefits to the collagen, and other attendant soft-tissue-building compounds, as grandma’s homemade stock. And there is a raft of scientific studies that bear this out.
But as with any supplement, the method of processing must be considered. Processing must protect the integrity of each individual compound that will wind up in the collagen supplement.
The best collagen supplements, therefore, begin with a whole-food product, like skin or joint material, and then employ gentle heat to break down (hydrolyze) the long, tough collagen molecules into shorter, easily digested chains, replicating the same processes that human being have used to maintain their joints, their skin and their overall health for millennia.
Collagen has been almost entirely removed from our diets. But make no mistake, it is essential. If there were anything worthy of the title of “youth serum,” collagen, and its associated compounds (like glucosamine and hyaluronic acid) would be it.

So whether it’s from bone stock or a top-tier collagen supplement (like what CB Supplements offer), my recommendation on collagen is simple: Get it in you.
You can save $5 on CB Supplements multi collagen protein when you use the coupon code “drcate”.
It’s the only supplement of any kind that I actually support and endorse.
Select Research on Collagen
Collagen is 5-10X stronger than steel: http://web.mit.edu/mbuehler/www/research/Collagen/summary_PNAS_Aug15.pdf
Proprietary blend shown to improve the appearance of aged skin: https://patents.google.com/patent/US20170231886A1/en
Proprietary blend shown to improve joint function
https://patents.google.com/patent/US8778422B2/en
Literature review from 2006 on collagen for joint health
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17076983/
A controlled human trial on knee joint symptoms
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33562729/
A controlled human trial on ankle joint symptoms
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5950747/
Please note: Please do not share personal medical information in a comment on our posts. It will be deleted due to HIPAA regulations.
This Post Has 10 Comments
Note: Please do not share personal information with a medical question in our comment section. Comments containing this content will be deleted due to HIPAA regulations.



















Hi Dr Cate
I have tried excellent quality powdered gelatin for when I don’t have a chance to make bone broth and to eat enough gelatin in my diet, every single time I get severely constipated. It is the only change I make and I have even tried half the dose. Same experience when trying collagen peptides!!
Any recommendations? Thank you so much!!!
That’s an unusual reaction, so sorry you’re dealing with it. My first conjecture is that it may be caused only by the dehydrated forms that negatively impact your gut flora. So maybe you could get the premade bone broths from Costco, which are so much less expensive that it may be worth joining just for that benefit.
This is the kind I recommend: Kirkland Signature Organic Chicken Bone Broth 32 fl oz, 6 ct
Another thought is there may be a chance that cartilage powder might not bother you. This is an example of what I mean by cartilage. https://kiwla.com/products/bovine-cartilage-180-caps-foodscience-of-vermont
If you can find it not encapsulated that would be cheaper. But it won’t dissolve in water easily that’s why its in capsules.
For theoretical reasons cartilage powder may actually be MORE effective than gelatin.
Wondering about us non meat eaters who eat wild fish such as salmon, cod, etc. I have tried this Marine Collagen powder – any thoughts?
https://www.nordic.com/products/marine-collagen/
Thanks!
Marine collagen seems to have worked for those living in Hawaii and other islands for thousands of years. The only caveat to that is that most island nations also supplemented with chicken and or pork, since pigs and chickens can travel on canoes.
My 30 yr old daughter suffered a fall and twisted both ankles about two yrs back. She has still not recovered properly. MRI taken few months after injury shows high grade tendinosis in both peroneus longus and peroneus brevis in both ankles along with more findings.
About 7-8 months back, she bent to pick something from floor and felt sudden pain in left lower chest, anterolateral surface. Since than she has trouble moving freely and she has to use rib band regularly. After many orthropedicians, she consulted a pain management specialist and he advised local injections. She refused.
Can you suggest something
As far as pain, we keep finding more evidence that seed oils promote chronic neuropathic pain and avoiding them allevaites at least some element of that kind of pain if not most or all.
Respected Mam,
Greetings
I am from India. More than 50% population here is pure vegetarian. How they get their collagen requirement fulfilled.
Is olive oil and canola oil are safe?
It’s not possible to get collagen on a vegan diet. Interestingly, 30 years ago when I traveled to Asia I was told by many people I quizzed about this that vegetarians mostly avoided beef and pork but ate fish and chicken. I suspect as the trend away from meat has continued, that has changed? The less protein and collagen you get, the more important it becomes to avoid seed oils, including canola. More info here: https://drcate.com/list-of-good-fats-and-oils-versus-bad/
Hey, thanks for writing this. I am wondering, are there any things to look out for as warning signs when looking to buy a collagen supplement? Or are most safe?
I got some from Unflavoured Collagen & Vitamin C from Bulk Powders as I’m UK-based. Ingredients: Hydrolysed Collagen (Bovine), Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid).
Would this be okay to take?
Thanks!!
Yes most are pretty safe. The fewer ingredients though the better. C is not useful, in spite of all the claims. Somewhat more detailed answer here: https://cbsupplements.com/cc/qa-collagen-more-effective-vitamins-minerals/#vitamin-c